Supercells are distinguished from other thunderstorms by their sustained and rotating updrafts, known as mesocyclones. These storms can persist for hours and are capable of producing severe weather conditions over wide areas.
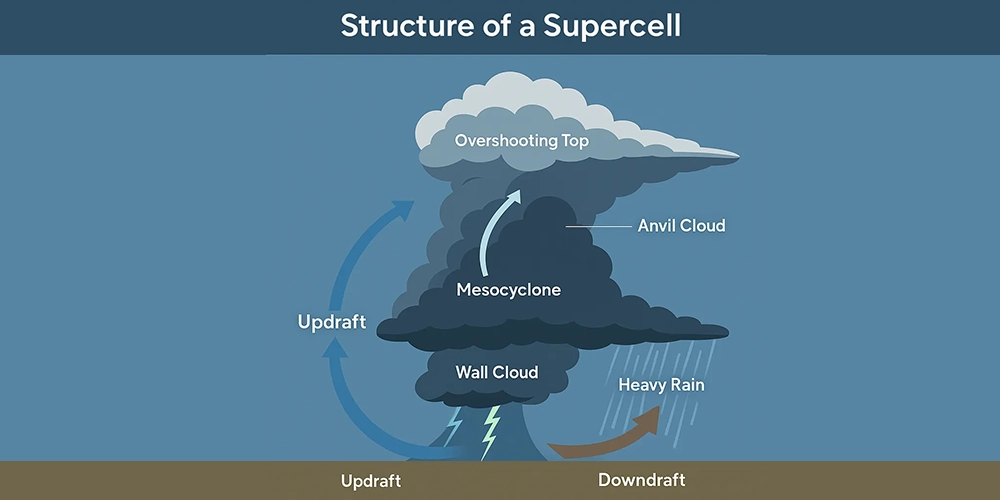
Key Features of a Supercell:
- Mesocyclone: A rotating column of rising air, visible on radar as a strong velocity couplet.
- Anvil Cloud: A flat, spreading cloud top that often extends downwind due to high-altitude winds.
- Overshooting Top: A dome-like bulge above the anvil, indicating intense upward motion.
- Wall Cloud: A lowering of the cloud base that can signal tornado development.
Types of Supercells:
- Classic Supercell: Produces all hazards—hail, wind, and tornadoes.
- Low-Precipitation (LP) Supercell: Minimal rain but high wind and hail potential.
- High-Precipitation (HP) Supercell: Heavy rainfall, reduced visibility, and flood risk.
Formation Conditions:
Supercells form when warm, moist air near the surface rises into colder, drier air aloft, in an environment with:
- Strong vertical wind shear
- High instability (CAPE)
- Lift from fronts or drylines
Why It Matters:
Supercells are responsible for most significant tornadoes and large hail events. Their long lifespan and violent behavior make them a focus for both research and forecasting efforts. Understanding how supercells behave is key to issuing timely warnings and reducing damage.
Buluttan’s Forecasting Advantage:
With AI-enhanced atmospheric modeling, Buluttan detects the conditions favorable for supercell formation earlier and more accurately. Our hyper-local alerts are designed to help cities, transportation systems, and emergency teams respond faster and more effectively.

